Server virtualization
During the last five years virtualization is becoming extremely popular. Why is it necessary for modern company?
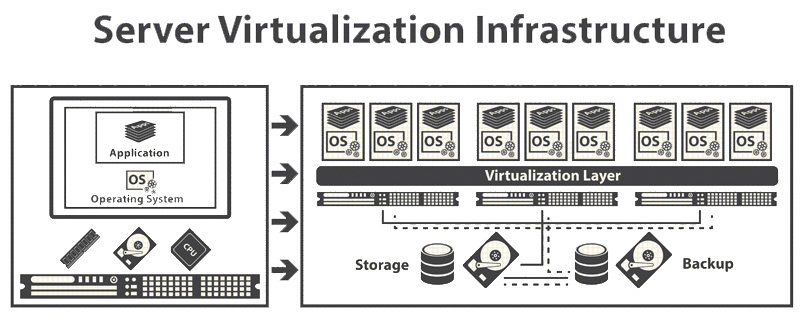
Virtualization is the transition from physical hardware to virtual. There are two main areas: a separate application virtualization and server virtualization. We will talk about server virtualization.
So what is the benefit?
The benefit is in saving space, electricity, power, cooling, network and server equipment. We used to have more than 400 physical servers — one server for one application. They occupied 8 stands. And now we have more than 3000 virtual servers. And they occupy only 4 incomplete racks.
In the end, the user works with programs. In most cases, programs can work with relatively weak equipment: 1-2 core, 1-8Gb RAM. Such servers mostly do nothing but wait for requests from users. Iron servers have become so powerful that their resource is enough for such small 20-30 virtual servers. It is only necessary to have enough memory and disk operations.
So what is the difference between physical server and virtual server (virtual machine)?
From the point of view of administration of the operating system and applications inside, they are pretty the same, except the lack of dependence on physical hardware. This means that you don't need to worry about compatibility with the physical hardware of the server, schedule downtime from having to upgrade the firmware and driver. And also to have a lot of downtime to replace or repair physical hardware. For maintenance of physical hardware on virtualization platform it's enough to move virtual servers to other available physical servers. It is done on the fly, transparent to the application. It should be noted that the application inside the server and the operating system itself must also be maintained. And if they don't allow you to perform maintenance without shutdown, the application will still have to be turned off.
We have passed a long way virtualizing servers and applications. We started over ten years ago, when there were only third Pentiums, and fourth Sparks. We used to just place several applications (mainly SAP) in large SF6900 and SF25K class servers. This enabled us to give the systems more resources than they could obtain on a separate, less powerful servers.
After that, we came to the conclusion that the systems should be isolated from each other — that is reasonable, first of all, for reasons of safety and from the point of view of computer resources. And we began using Solaris Zones (and still use them on the remaining SF25K). On this way we have encountered several technical difficulties. For example, we realized that the swapping just "kills" the physical server and affects all systems. So we rejected any limitation of physical memory on SPARC.
Our system grew, and they began lacking space, even within a huge SF25K. We were looking at the different super-servers, but eventually switched to x86 virtualization based on VMware license. By that time we already had experience hosting about 300 machines on VMware 3. We transferred some of the application servers and terminal servers on a virtual platform. And then began to place new systems on it and gradually move systems on it from SF25K.
Now there are more than 3,000 virtual servers on our platform in multiple data centers. Some of them are very powerful — for example, one of the SAP systems is demanding more resources collectively than the good old SF25K actually posessed — the system is able to accommodate on a pair of blades, and SF25K takes up the space of one and a half racks. There are Oracle instances with a storage capacity of almost 200GB. And it all fits together in part-4 racks. And all the space in the data center is taken by drives, drives, and drives again. This is the nowadays trend - there is becoming more information, but most importantly, more and more information must be processed. And it means reading and writing drives — IOPS's, IOPS's, and more IOPS's.
The typical evolution of any equipment: it is super-leading now, a year later it is "still fine", and after 2-3 another years it is already at the secondary level. The same with storage systems. And the number of information systems keeps growing. They require more and more resources. But you can't throw out the outdated storage system that regularly stores hundreds of TB of data but displays only a few thousand IOPs. This space can be useful in the virtual environment. The new storage systems keep appearing. Many of them allow you to connect older storage systems and on their behalf to provide them the space - virtualization of storage systems. What is the use of it? It is the protection of investments made before.
We have worked with the systems from a number of vendors: Hitachi, SUN, NetApp, HP, RCNTEC. And we have extensive experience in working with each storage system and in their integration.
In this way we developed the platform of one of our largest customers, LUKOIL-INFORM. We follow this platform even now. But, however, we provide hosting, based on virtualization platform KVM to other customers as well.
The main advantage of virtualization is the reduction of time of server allocation to the client. In most large companies there is an annual cycle of investment planning for the purchase of equipment. This is, firstly, means that the acquisition of equipment for the this year project was supposed to be scheduled last year. Secondly, buying of physical equipment in most cases requires placing order in production — delivery time is increased to 8 weeks. The allocation of the virtual servers happens almost instantly. It is only necessary to have a renewable supply of server capacity.
High Availability allow you to restart the virtual server on another physical server within minutes if the failure of a physical hardware happens. And if you configure the autostart for application inside the server, it starts automatically when the server starts.
Backup and restoration of servers become easier. You are not tied to physical hardware so you can quickly migrate virtual server from one data center to another.
Yes, virtualization saves a lot of money due to the absence of the need to purchase physical servers, communication equipment and engineering systems if you want to deploy new servers. But building of your own virtual environment Enterprise level will require considerable effort, time, cost, involvement of consulting, since a good infrastructure is the basis for the further development of your business.
The alternative is ordering virtual servers from a hosting company (like us :) ). We specialize in server virtualization. We can also offer and administer operating systems, databases and applications. Taking backup. You can also take advantage of our centralized monitoring system.
This is a truly unique creation —we created this system for our own needs, and most of our customers enjoy it. The system allows you to build a hierarchy of dependencies of information systems. At some point it was not enough just to monitor the availability of servers, and we began to monitor the information systems: databases, applications. When the operation fails, the administrator looks through the components in turn from the most obvious to the least likely, checking them on different parameters. We thought how to make troubleshooting easier? Let the parameters of all components to be checked automatically! And not only after a failure, but constantly — and we will see the prerequisites of possible failure, and we will know what exactly is broken. The second important part is immediately show, what exactly is out of order. Usually when the information system is developed in-depth, it consists of dozens of components (servers, systems, databases, applications) — even if they are directly displayed on the 50 inches monitor — some are red, another are green, third are yellow, it is very hard to find the root cause of all failures. So we did the obvious — got rid of all the components that are in order at this time (green). When the operation fails, the hierarchy is revealed to the failed component, indicating the reason (which of the tests didn't pass), indicating the contact information of the administrator responsible for the component.
This information on all the monitored systems of our customers is displayed on the monitors of the situation centre of the Department of quick response — our round-the-clock service for resolving the incidents. They can either choose to eliminate the consequences of failures, or to connect the administrators in difficult cases.
We are happy to help you with building of your own online platform and its services. We also offer server hosting based on our virtual platform.
Feel free to contact us at any time!
